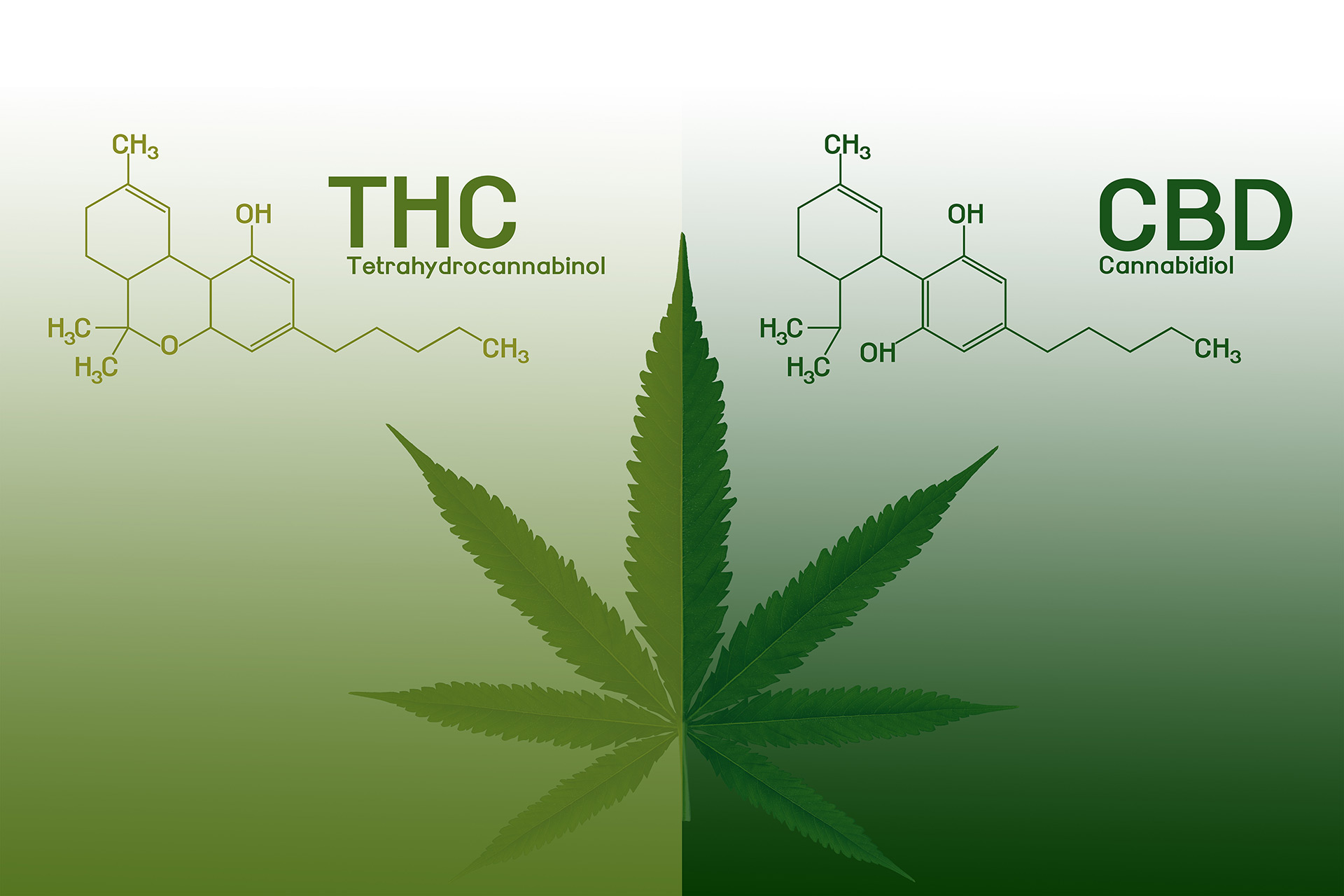
Very simply, we can say that the term cannabinoid generically refers to one of the substances found or extracted from Cannabis Sativa. Plant of the genus angiosperm of the family cannabaceae and in which there are about five hundred chemical compounds. Among them more than one hundred and twenty identified phytocannabinoids, produced by tiny, glandular structures found on the plant’s surface: the trichomes.
Of all this sparsely explored, natural repertoire of Cannabis Sativa, the two substances most seriously studied by science worldwide are cannabidiol or CBD and tetrahydrocannabinol or THC. Both have the same molecular structure with a subtle change in the organization of atoms that makes their properties noticeably different.
Combined, these substances promote better results.
CBD, for example, has no intoxicating action and therefore does not cause any change in the perception of reality. It stands out mainly for its analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anxiolytic, antidepressant, neuroprotective, anticonvulsant and anti-nausea properties. It is also a bone stimulant and neuroprotective. In addition to modulating the performance of THC related to unwanted effects such as anxiety, depression or hallucinations.
THC, on the other hand, has a widely known psychoactive action, characterized by the feeling of euphoria and loss of recent memory, although it has very important medicinal properties. It is a potent appetite stimulant, muscle relaxant, sedative, analgesic and anti-inflammatory. It also acts on chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, in addition to having a positive effect on mood. Even so, side effects such as anxiety, depression, momentary increase in heart rate and loss of recent memory can be impeding for certain patients and contraindicated in some situations.
However, the side effects of THC are considerably reduced when using CBD-rich compositions. Cannabidiol has a pharmacological property, which when used with THC prevents the main unwanted side effects like anxiety and paranoia.
References:
- Pharmacogenetics of Cannabinoids. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2018 Feb;43(1):1-12. doi: 10.1007/s13318-017-0416-z.
- Medical Use of Cannabinoids. Drugs. 2018 Nov;78(16):1665-1703. doi: 10.1007/s40265-018-0996-1.
- Beyond Cannabis: Plants and the Endocannabinoid System. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2016 Jul;37(7):594-605. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2016.04.005. Epub 2016 May 11.
- Cannabis Roots: A Traditional Therapy with Future Potential for Treating Inflammation and Pain. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2017 Aug 1;2(1):210-216. doi: 10.1089/can.2017.0028. ECollection 2017.